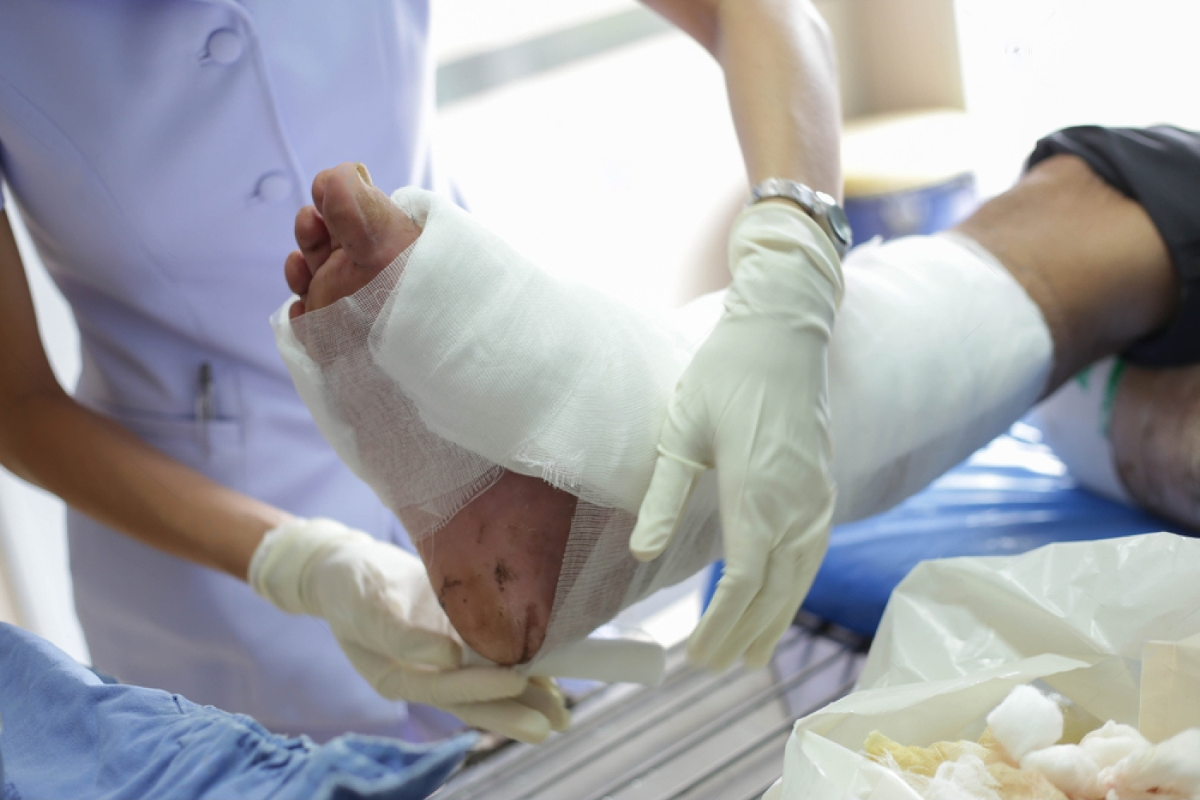
Understanding Infected Wounds and Orthopedic Concerns
Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is a highly specialized area of care that addresses not only the wound itself but also the underlying bones, joints, and soft tissues. An infected wound differs from a typical injury because bacteria or other harmful organisms invade the wound site, causing swelling, pain, and delayed healing. This complication becomes even more serious when it involves orthopedic injuries such as fractures, surgical incisions, or trauma to muscles and bones. Orthopedic specialists play a crucial role in managing these cases, as their expertise ensures that infections do not compromise bone stability or long-term mobility. If left untreated, infected wounds can lead to dangerous outcomes like sepsis or bone deterioration. Patients often underestimate the seriousness of an infected wound, but without proper orthopedic intervention, complications may extend far beyond the skin and soft tissues. This is why seeking specialized care from an orthopedic professional is essential for full recovery.
How Infections Develop in Orthopedic Injuries
Infections in orthopedic injuries typically occur when bacteria enter through broken skin, surgical incisions, or puncture wounds that reach deep tissue layers. Open fractures are particularly vulnerable, as the bone is exposed and prone to contamination. Other risk factors include poor circulation, diabetes, and weakened immune systems, all of which limit the body’s ability to fight infection effectively. Patients may notice common warning signs such as redness, swelling, pus discharge, increased pain, or warmth around the wound site. In more severe cases, fever or chills may develop, signaling that the infection has spread. Orthopedic infections can also be classified as acute, occurring within days of the injury, or chronic, where the infection lingers for months and can damage bone tissue. Understanding how infections develop allows patients and caregivers to act quickly and seek professional medical care before complications worsen.
Diagnostic Steps in Orthopedic Treatment for Infected Wounds
Accurate diagnosis is the foundation of effective orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. Orthopedic specialists typically begin with a detailed physical examination, checking the wound’s appearance, discharge, and surrounding tissues. Laboratory testing is often used to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection, which helps in prescribing the right antibiotics. Blood tests may also reveal elevated white blood cell counts or markers of inflammation. Imaging tools such as X-rays or MRI scans are valuable in detecting whether the infection has spread to the bone, a condition known as osteomyelitis. Early diagnosis is especially important because delays in treatment increase the risk of complications and long-term damage. The combination of physical assessment, laboratory analysis, and imaging allows doctors to create a tailored treatment plan. Patients benefit from this comprehensive diagnostic approach because it ensures that the chosen therapy targets the infection effectively while supporting overall healing.
Non-Surgical Orthopedic Treatments for Infected Wounds
When orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is initiated early, many patients respond well to non-surgical methods. Antibiotics are the first line of defense, with doctors selecting specific medications based on the bacteria identified in laboratory tests. Local wound care is equally important and often includes cleaning, debridement to remove dead tissue, and frequent dressing changes. Advanced methods such as negative pressure wound therapy can help stimulate blood flow and promote faster healing. Pain management strategies are also included in the care plan, ensuring that patients remain comfortable during recovery. Follow-up visits allow orthopedic specialists to monitor progress, adjust treatments, and prevent the infection from worsening. Patient education is critical at this stage, as proper wound care at home greatly improves the chances of recovery. These non-surgical interventions can often control infections effectively, but they must be carefully managed under professional supervision.
Surgical Options in Orthopedic Treatment for Infected Wounds
For severe or persistent infections, surgical treatment becomes necessary to save the affected bone and surrounding tissues. One common procedure is incision and drainage, where the surgeon removes pus and infected tissue to allow healing. In cases where bone is involved, surgical debridement may be required to cut away infected portions while preserving as much healthy bone as possible. Some patients may require reconstructive surgery to repair soft tissue or bone damage caused by the infection. If the infection occurs near orthopedic implants such as screws, rods, or prosthetic joints, specialized techniques are needed to treat or replace the devices. Post-surgical recovery includes continued antibiotic therapy, wound care, and rehabilitation exercises to restore strength and mobility. Preventing re-infection is a primary goal, and this often requires a combination of medical management and lifestyle adjustments. Surgical options can be life-saving, ensuring that patients regain mobility and avoid long-term disability.
Preventive Measures in Orthopedic Care for Wounds
Prevention plays a critical role in orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. Proper wound hygiene, including thorough cleaning and the use of sterile dressings, significantly reduces the risk of infection. Orthopedic surgeons implement strict infection control strategies before and after surgery to protect patients from bacterial contamination. Patients are also encouraged to adopt healthy habits such as eating nutrient-rich foods, staying hydrated, and avoiding smoking, as these factors directly impact the body’s ability to heal. For individuals with conditions like diabetes, maintaining stable blood sugar levels is essential to reduce infection risk. Physical therapy may also be recommended, not only to restore movement but also to improve circulation, which supports faster healing. Preventive measures require a partnership between patients and healthcare providers, with education playing a key role in minimizing risks. When prevention is prioritized, patients are more likely to recover smoothly from orthopedic injuries and surgeries.
Long-Term Impact of Untreated Infected Wounds on Orthopedic Health
Failing to address infected wounds can lead to serious long-term consequences. Chronic infections may damage bone and cartilage, leading to conditions like osteomyelitis, which are difficult to treat and often require extensive surgery. In severe cases, untreated infections can spread to the bloodstream, causing life-threatening sepsis. Patients may also experience reduced mobility, joint stiffness, or long-term pain, which significantly impacts quality of life. For some, the damage may become so severe that amputation becomes the only option. Beyond physical consequences, the emotional toll of living with a chronic infection can be overwhelming, leading to anxiety or depression. These outcomes highlight the importance of early and consistent orthopedic care for infected wounds. By seeking timely treatment, patients not only avoid serious complications but also preserve their independence and daily functionality.
When to Seek an Orthopedic Specialist for Infected Wounds
Knowing when to see a specialist can make a significant difference in outcomes. Patients should seek immediate orthopedic evaluation if wounds show signs of spreading redness, persistent pain, or foul-smelling discharge. Fever, chills, or fatigue may also indicate that the infection is becoming systemic and requires urgent care. Unlike general practitioners, orthopedic specialists have the expertise and tools to manage infections that affect bones and joints. They can provide advanced treatments that prevent lasting damage and improve long-term recovery. Timely referral to an orthopedic clinic ensures patients receive specialized wound management, surgical options when necessary, and comprehensive rehabilitation support. For those recovering from orthopedic surgery or fracture treatment, regular follow-ups are critical to detect and address infections early. By consulting an orthopedic specialist at the first sign of complications, patients take proactive steps toward protecting their mobility and overall health.
FAQ Section
Q1: What are the first signs of an infected orthopedic wound?
The earliest signs include redness, swelling, warmth around the wound, and discharge of pus. Pain that worsens instead of improving and fever may also indicate infection.
Q2: How long does it take for an infected wound to heal with orthopedic treatment?
Healing time varies depending on the severity of the infection and the patient’s overall health. Mild infections may resolve in weeks, while complex bone infections may take several months.
Q3: Can orthopedic wound infections be treated without surgery?
Yes, many infections respond to antibiotics, wound cleaning, and advanced dressings. However, surgery is sometimes required for deep or persistent infections.
Q4: What role do antibiotics play in orthopedic wound care?
Antibiotics are central to controlling bacterial infections. They may be given orally or intravenously, depending on the infection’s severity.
Q5: Are infected wounds around orthopedic implants more difficult to treat?
Yes, infections near implants present additional challenges. Treatment may involve both antibiotics and surgical procedures to clean or replace the implant.