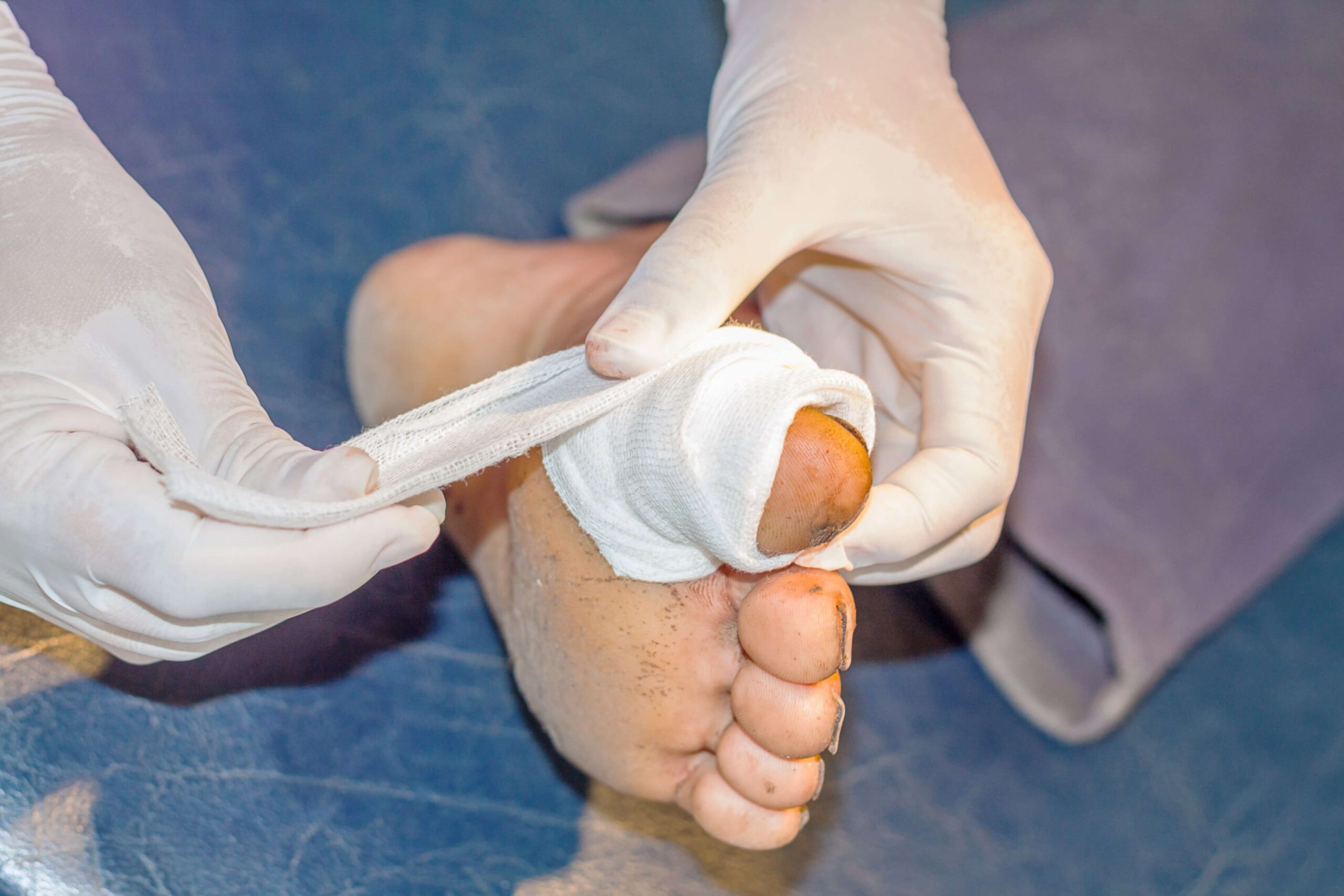
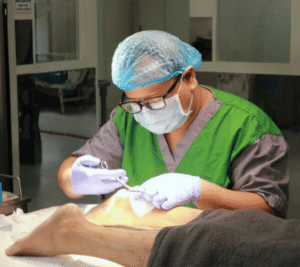
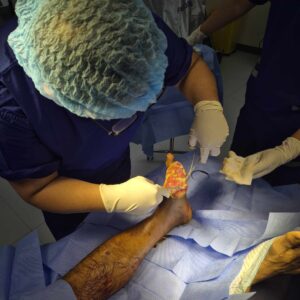
Diabetic foot wounds that refuse to heal pose serious health risks and may lead to severe complications if not addressed properly. Patients living with diabetes face unique challenges because high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, making even minor injuries problematic. Orthopedic treatment for non-healing foot wounds in diabetes offers specialized care that targets infection control, careful tissue management, and improved mobility, ultimately aiming to secure better long-term outcomes.
Understanding Diabetic Foot Wounds
Foot wounds in individuals with diabetes commonly develop due to a combination of reduced blood flow and nerve damage. Over time, persistently elevated blood sugar levels can injure the small blood vessels responsible for supplying oxygen and nutrients to the foot tissues. This injury, paired with neuropathy—or the loss of sensation—means that minor injuries may go unnoticed until they become severe. As the body’s natural healing processes are compromised, wounds fail to close and can become chronic.
A persistent wound not only risks turning into a serious infection but also affects overall foot function. These wounds often require more than simple wound care because the underlying issues, such as poor circulation and nerve impairment, must also be managed. Diabetic patients are advised to perform regular self-checks, keep their feet clean and dry, and wear proper footwear to avoid small cuts and blisters that might escalate into larger problems. Early recognition and treatment are critical, as delayed care can lead to complications including tissue death or the need for surgical intervention.
The Role of Orthopedic Treatment
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing foot wounds in diabetes plays a vital role in addressing the complexities of this condition. Orthopedic specialists possess the expertise necessary to evaluate both the wound and the surrounding structures, such as bones, muscles, and tendons. Their approach is not solely focused on closing the wound but also on restoring the overall function of the foot.
Specialists begin by assessing the wound’s depth, size, and location, along with any signs of bone involvement or compromised circulation. Advanced imaging techniques and thorough clinical evaluations help determine the full extent of the injury. This detailed assessment lays the groundwork for a personalized treatment plan that may include surgical procedures, debridement (the careful removal of dead tissue), and specialized wound care techniques.
A key objective in these cases is to arrest the progression of the wound while simultaneously preventing further complications. Orthopedic care teams work to stabilize the foot structure, manage infection risks, and promote an environment where the natural healing processes can proceed more effectively. Their expertise often makes the difference between a successful recovery and the potential loss of a limb.
Infection Management Strategies
Infections are a common and dangerous complication associated with non-healing diabetic foot wounds. Poor blood supply in affected areas hampers the body’s ability to fight off bacteria, making infections more likely and more severe. Orthopedic specialists use a combination of methods to manage and control infections.
First, early detection of infection is essential. Patients are advised to monitor their wounds for signs such as increased redness, warmth, swelling, or discharge. Once an infection is suspected, physicians may order laboratory tests and imaging studies to identify the specific bacteria involved and to assess the extent of the infection.
Treatment usually begins with the administration of antibiotics. In some cases, however, the infection may be too advanced for medications alone, and surgical debridement becomes necessary. This procedure involves the careful removal of necrotic (dead) tissue, which not only reduces the bacterial load but also encourages the healing of surrounding healthy tissue. The combination of antibiotic therapy and timely surgical intervention helps reduce the risk of severe complications such as osteomyelitis (bone infection).
A multidisciplinary team often oversees infection management. Orthopedic surgeons collaborate with infectious disease experts to determine the most effective antibiotic regimen and to monitor the patient’s response to treatment. Regular follow-up appointments ensure that the infection is responding to therapy and that the wound is on a path to recovery.
Tissue Preservation Approaches
The preservation of healthy tissue around the wound is as crucial as treating the wound itself. Removing damaged or infected tissue is necessary, yet it must be done with care to maintain as much viable tissue as possible. This balance is especially important in diabetic patients, where the ability to regenerate tissue is already compromised.
Orthopedic teams utilize precise debridement techniques to excise dead tissue while sparing healthy cells. This approach promotes natural healing by reducing the burden on the body’s repair mechanisms. In some cases, advanced treatments such as negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) may be used. NPWT applies controlled suction to the wound, which helps remove excess fluid and stimulates blood flow, further supporting tissue repair.
Maintaining the integrity of the foot’s structure is a significant focus during treatment. By preserving healthy tissue, the likelihood of a successful recovery increases, and patients may experience improved long-term functionality. The careful balance between removing harmful tissue and conserving healthy cells is a testament to the precision required in managing chronic diabetic wounds.
Enhancing Mobility and Function
A major goal in managing non-healing foot wounds is to restore and preserve mobility. Pain, discomfort, and the fear of further injury often limit the movement of individuals with chronic wounds. Orthopedic specialists incorporate rehabilitation into their treatment plans to address these issues and improve overall function.
Physical therapy plays a central role in this process. Therapists design exercise programs that promote blood flow, strengthen muscles, and improve balance. These programs are customized to each patient’s specific needs and physical condition, taking into account the severity of the wound and any other complications that might be present.
Custom orthotics and assistive devices are frequently recommended to redistribute pressure away from the injured area. Such devices not only reduce pain but also help prevent further damage to the healing tissue. Orthopedic providers work closely with rehabilitation experts to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as the patient’s condition evolves.
By focusing on mobility, treatment plans support a quicker return to daily activities and help restore independence. Patients who engage in regular, supervised physical therapy sessions often report improvements in their overall quality of life, with reduced pain and better function of the affected limb.
Prevention and Early Detection
Preventing the occurrence of non-healing foot wounds is critical for diabetic patients. Routine foot care can help minimize the risk of developing wounds that may escalate into chronic conditions. Simple practices such as daily inspections, proper washing and drying of the feet, and wearing shoes that fit correctly can make a significant difference.
Health care providers emphasize the importance of early detection. Patients should look out for any changes in the skin, such as discoloration, dryness, or the appearance of cracks. Promptly addressing these issues with a health professional can help prevent minor problems from developing into major wounds.
Regular check-ups are an essential component of preventive care. Diabetic patients benefit from frequent visits to both their primary care physicians and specialists who are experienced in foot care. These appointments provide opportunities for early intervention and ensure that any potential issues are managed before they become severe.
Educational programs and community support initiatives also play a role in prevention. By learning proper foot care techniques and recognizing the warning signs of a wound, patients are better equipped to manage their condition and avoid complications. A proactive approach to foot health can reduce the incidence of non-healing wounds and improve overall well-being.
Choosing the Right Orthopedic Provider
Selecting an experienced orthopedic specialist is critical for successful treatment. When evaluating potential providers, patients should consider factors such as the specialist’s experience with diabetic foot wounds, the availability of advanced treatment technologies, and the ability to work as part of a coordinated health care team.
A provider who specializes in diabetic foot care will be well-versed in the latest treatment protocols and surgical techniques. It is beneficial to seek out clinics or practices with a multidisciplinary approach, where orthopedic surgeons, wound care experts, and rehabilitation therapists collaborate closely. This coordinated effort can lead to a more comprehensive and effective treatment plan.
Patient testimonials and case studies often offer valuable insights into a provider’s track record. Reading about the experiences of others who have undergone similar treatments can help patients feel more confident in their decision. Taking the time to research and select the right provider is an investment in long-term health and mobility.
Takeaway
Chronic foot wounds in diabetic patients represent a multifaceted challenge that demands specialized care. Orthopedic treatment for non-healing foot wounds in diabetes addresses the root causes of impaired healing by focusing on infection control, precise tissue management, and the restoration of mobility. Through a combination of advanced surgical techniques, careful wound care, and tailored rehabilitation programs, orthopedic specialists strive to improve the quality of life for patients facing these complications.
Patients who remain attentive to their foot health and engage in regular preventive practices have a better chance of avoiding severe complications. When issues do arise, early intervention by an experienced orthopedic provider is essential. By embracing a comprehensive treatment plan, patients can reduce the risk of infections, preserve healthy tissue, and regain mobility—all critical factors for maintaining independence and overall well-being.