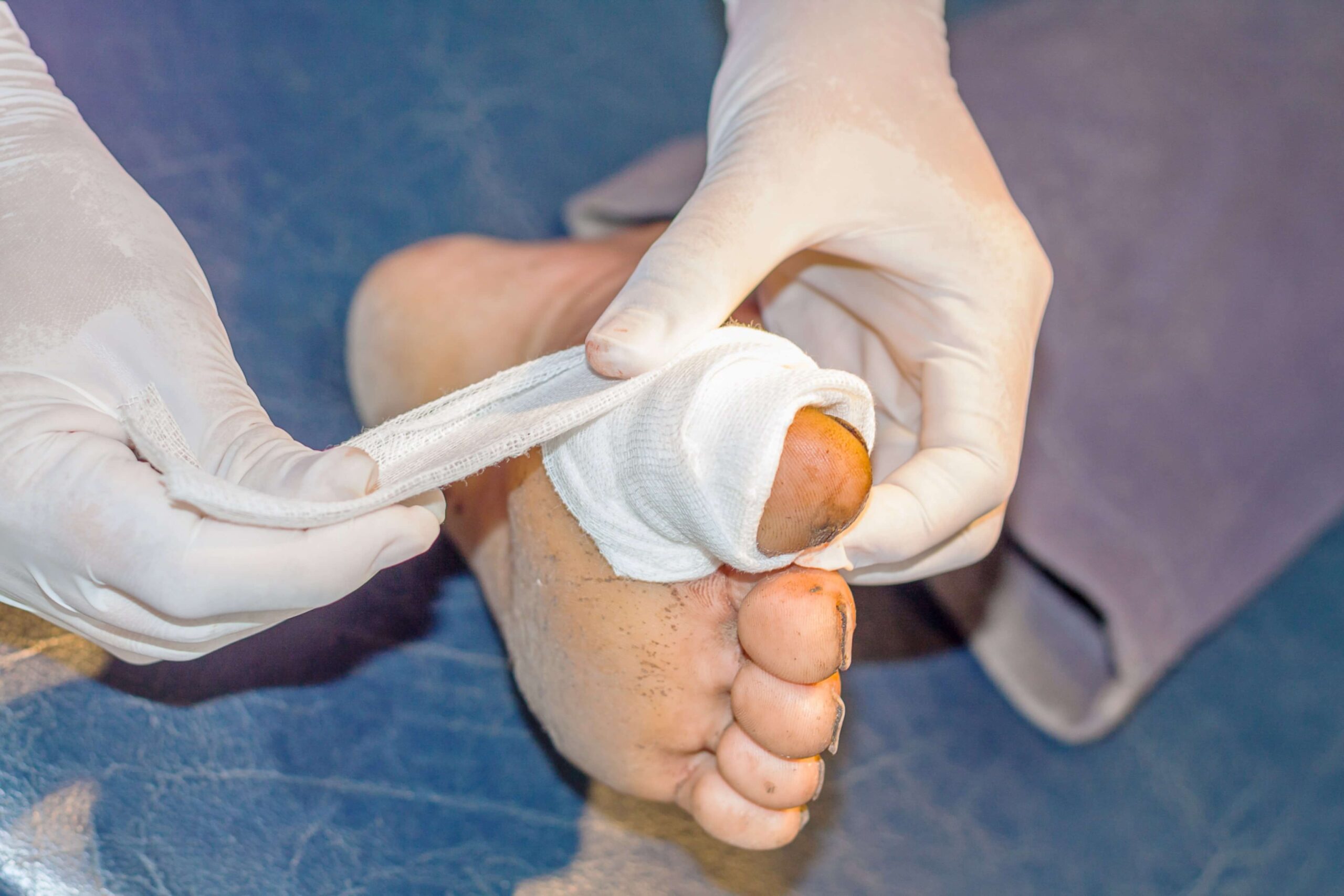
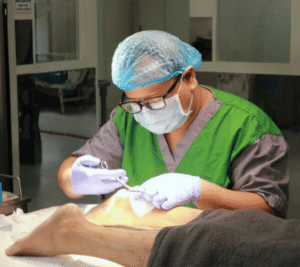
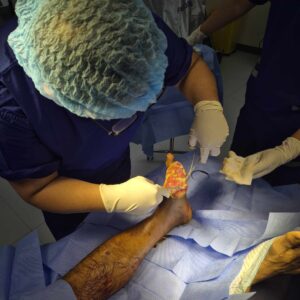
Diabetes-related foot infections present a significant risk for individuals managing elevated blood sugar levels. When wounds fail to heal properly, they can lead to severe complications that compromise mobility and quality of life. Orthopedic Treatment for Diabetes-Related Foot Infection involves a focused method of infection control, preservation of healthy tissue, and therapeutic strategies that support weight-bearing activities. Through early intervention and coordinated care, patients benefit from reduced likelihood of amputation and improved long-term function.
What Causes Non-Healing Foot Wounds in Diabetes?
Non-healing foot wounds emerge when minor injuries or ulcers do not close due to disrupted blood flow and nerve damage. In diabetes, elevated glucose levels damage small blood vessels, which impairs circulation in the lower limbs. Neuropathy reduces sensation, allowing minor cuts or pressure sores to progress without detection. Common triggers include:
- Peripheral arterial disease: Narrowed arteries reduce delivery of oxygen and nutrients to tissues.
- Diabetic neuropathy: Loss of protective sensation leads to unrecognized injuries.
- Foot deformities: Bony prominences or changes in foot structure create pressure points.
- Poor wound care: Inadequate cleaning and dressing allow bacteria to thrive.
Addressing these root causes through vascular assessment and lifestyle adjustments is a key step in preventing chronic ulcers.
Signs and Symptoms of a Diabetic Foot Infection
Identifying early warning signs is essential. Patients should monitor for:
- Localized redness and warmth: Inflamed tissue around a wound often signals infection.
- Swelling or edema: Fluid accumulation can indicate inflammatory response.
- Discharge or pus: Thick fluid or foul odor suggests bacterial growth.
- Systemic symptoms: Fever, chills, or elevated heart rate may accompany severe infections.
If any of these signs appear, prompt evaluation by an orthopedic specialist can prevent deeper tissue involvement.
Orthopedic Assessment and Diagnosis
A detailed evaluation helps determine the extent of infection and guides treatment:
- Vascular studies. Doppler ultrasound assesses blood flow, revealing areas of poor perfusion that hinder healing.
- Imaging scans. X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging show bone involvement and detect osteomyelitis.
- Laboratory tests. Wound cultures identify causative bacteria, while blood tests measure inflammatory markers such as C‑reactive protein (CRP) and white blood cell count.
Combining these diagnostic tools allows clinicians to plan targeted therapies and monitor progress objectively.
Infection Management Strategies
Effective infection control relies on a combination of surgical and medical approaches:
- Debridement. Removing dead or damaged tissue reduces bacterial load and exposes healthy margins for healing.
- Antibiotic therapy. Culture-guided administration of systemic antibiotics ensures coverage of identified organisms. In some cases, local antibiotic delivery via impregnated beads or dressings accelerates eradication.
- Negative-pressure wound therapy. Controlled suction over the wound bed promotes granulation, reduces edema, and helps remove exudate.
Regular wound assessments and antibiotic adjustments based on culture results are essential until signs of infection resolve.
Techniques for Tissue Preservation
Maintaining viable tissue around the wound helps minimize the size of the defect and supports faster repair:
- Offloading devices. Customized orthotic inserts or total contact casts redistribute pressure away from vulnerable areas, protecting the wound margin.
- Advanced wound dressings. Moisture-retentive coverings maintain an ideal healing environment. Some dressings include antimicrobial agents like silver or iodine to discourage bacterial growth.
- Biologic therapies. Application of growth factors or skin substitutes provides scaffolding for cellular regeneration.
By preserving as much healthy tissue as possible, orthopedic specialists reduce the need for extensive surgical reconstruction.
Restoring and Maintaining Mobility
Regaining safe ambulation is a gradual process supported by tailored therapy plans:
- Physical therapy. Guided exercises improve muscle strength, joint range of motion, and balance; therapists introduce progressive weight-bearing based on wound status.
- Gait training. Focused practice on correct walking patterns prevents compensatory movements that could create new pressure points.
- Assistive devices. Walkers, canes, or specialized diabetic footwear offer stability and further offload stress from healing areas.
Collaborative sessions with physical therapists and orthopedic providers ensure that activity levels increase without compromising wound closure.
Preventing Recurrence and Long-Term Care
Ongoing strategies help patients keep wounds from returning:
- Daily foot inspections. Patients learn to examine soles and between toes for early signs of pressure or injury.
- Skin care routines. Gentle cleansing, moisturization of dry areas, and careful trimming of nails reduce risks.
- Glycemic control. Collaborating with primary care and endocrinology teams to achieve target blood sugar targets lowers vascular and nerve damage progression.
- Scheduled follow-ups. Regular visits to a multidisciplinary clinic allow experts in vascular surgery, podiatry, and orthopedics to address emerging concerns quickly.
Education and support services empower patients to maintain foot health as part of their overall diabetes management.
Takeaway
Ultimately, a proactive approach to Orthopedic Treatment for Diabetes-Related Foot Infection can mean the difference between a minor setback and a life-altering complication. By combining precise infection control measures, careful preservation of healthy tissue, and customized mobility support, patients stand the best chance of healing fully while maintaining independence.
Recognizing warning signs early and seeking specialized orthopedic evaluation ensures tailored interventions—such as surgical debridement, antibiotic regimens guided by cultures, advanced offloading techniques, and rehabilitative therapy—are applied before an infection escalates. Ongoing education, daily foot care routines, and coordinated follow‑up within a multidisciplinary team further safeguard against recurrence.
Tec Orthopedics is dedicated to guiding individuals through every stage of this journey, from initial assessment through restored ambulation. If you or a loved one is facing a stubborn foot wound, reach out today to explore how expert orthopedic treatment can support lasting healing and renewed confidence on your feet.