Diabetic foot wounds present an especially challenging complication for many individuals with diabetes. The complexity of these wounds arises from poor circulation, neuropathy, and the increased risk of infections, which, if left untreated, can lead to serious complications, including gangrene. Expert care is essential to manage these wounds effectively. This article delves into the importance of Orthopedic Treatment for Foot Wounds that Won’t Heal in Diabetes, outlines how specialized treatments help address these complications, and offers strategies for maintaining long-term foot health.
Understanding the Challenges of Diabetic Foot Wounds
Diabetic foot wounds are open sores or ulcers that typically develop on the bottom of the feet. They often begin with minor trauma or pressure points and do not heal effectively due to compromised blood flow and nerve damage (neuropathy). The reduced sensation can prevent individuals from recognizing injuries early, while poor circulation impedes the natural healing process.
Common Complications
For people with diabetes, non-healing foot wounds often evolve into more severe complications, such as:
- Infections: The body’s diminished immune response struggles to fight off pathogens.
- Gangrene: Prolonged poor circulation can lead to tissue death, which may progress to gangrene if not properly managed.
- Impaired Mobility: Persistent pain and wound complications can hinder movement, impacting a patient’s overall quality of life.
Understanding these complications is essential because they underscore the urgency and importance of early intervention. When left unattended, the wounds can escalate quickly, making them life-altering or even limb-threatening conditions.
Why They Don’t Heal
Several underlying factors contribute to the poor healing of diabetic foot wounds:
- Vascular Issues: The inadequate supply of oxygen and nutrients due to impaired circulation significantly slows down the repair process.
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage reduces the sensation in the feet, meaning that even minor injuries may go unnoticed until they have worsened.
- Continuous Pressure: Daily activities, especially without proper footwear, place continual stress on the affected area, further delaying recovery.
- Immune Response: Diabetes can weaken the immune system, limiting the body’s ability to fight infections effectively.
The convergence of these factors makes early, comprehensive orthopedic intervention not just beneficial but necessary.
The Crucial Role of Orthopedic Treatment in Diabetic Foot Wounds
Orthopedic Treatment for Foot Wounds that Won’t Heal in Diabetes encompasses a comprehensive approach that includes both surgical and non-surgical interventions. Orthopedic specialists frequently work together with endocrinologists, podiatrists, and vascular specialists to create an integrated treatment plan. This teamwork ensures that all aspects of wound care are addressed—from reducing pressure on the wound to preventing further tissue damage.
Primary Treatment Goals
The treatment approach is centered on three main objectives:
- Preventing Infection: Since infection is a major concern for diabetic foot wounds, interventions are designed to minimize bacterial exposure and promote a sterile healing environment.
- Preserving Tissue Integrity: Protecting the surrounding healthy tissues is critical. This involves debridement (the removal of dead tissue) and the use of advanced dressings to aid tissue regeneration.
- Improving Mobility: Treatments are structured to reduce pain and restore function, ensuring that patients regain as much movement and independence as possible.
Each of these goals is addressed with specific techniques that are tailored to the patient’s condition. The outcome is a treatment plan that not only focuses on the immediate issue of the wound but also the overall health and mobility of the patient.
Advanced Treatment Techniques
Several advanced techniques are used in the management of non-healing foot wounds among diabetic patients:
- Debridement: This technique involves the careful removal of necrotic (dead) tissue, which helps reduce the bacterial load and allows the body’s natural healing processes to take over. Regular debridement sessions can significantly accelerate the healing process.
- Offloading Devices: Specialized footwear or orthotic devices help relieve pressure from the wound area. By redistributing weight away from the affected region, these devices allow the wound to heal without the added strain of daily activities.
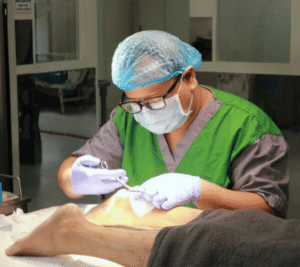
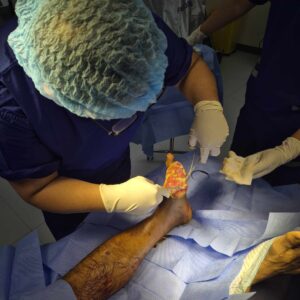
- Surgical Interventions: In severe cases where non-invasive methods do not provide the necessary healing support, surgical procedures may be required. These procedures aim to restore blood flow, remove infected tissues, or even reconstruct affected areas.
- Adjunct Therapies: Treatments such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy can be used to enhance oxygen delivery to the affected tissues, further aiding the healing process.
Real-Life Success Stories in Diabetic Foot Wound Management
Hearing from real patients can be inspiring and informative. Consider a patient who suffered from a chronic foot wound for months due to underlying diabetic complications. After receiving a tailored treatment plan involving regular debridement and the use of offloading devices, the wound began to show remarkable improvement. The patient not only experienced decreased pain and inflammation but also saw enhanced mobility, which allowed for a return to daily activities and an improved quality of life.
Another success story involves a case where surgical intervention was necessary to restore adequate blood flow. Post-surgery, the orthopedic treatment plan, combined with diligent wound care and follow-up, resulted in a significant turnaround. These case studies highlight the tangible benefits of Orthopedic Treatment for Foot Wounds that Won’t Heal in Diabetes and the positive impact it can have on patient outcomes.
Preventative Measures and Strategies for Long-Term Foot Health
Daily Foot Care Routines
Maintaining proper foot care routines is a cornerstone in preventing the development or worsening of diabetic foot wounds. Daily practices should include:
- Routine Inspection: Regularly checking for cuts, blisters, or any sign of irritation can lead to early detection and intervention.
- Appropriate Footwear: Shoes that fit well and provide adequate support can prevent pressure points and blisters. In some cases, custom orthotics are recommended.
- Proper Hygiene: Keeping the feet clean and moisturized helps maintain skin integrity and reduces the risk of cracking and infection.
Managing Diabetes Effectively
Overall diabetes management plays a critical role in preventing complications associated with non-healing foot wounds. Effective strategies include:
- Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is essential to prevent the vascular and nerve damage that contributes to poor wound healing.
- Healthy Diet and Exercise: A balanced diet and regular physical activity help support overall health, improve circulation, and reduce the risk of complications.
- Medication Adherence: Taking medications as prescribed by healthcare providers helps manage diabetes and prevents the progression of complications.
Regular Medical Follow-ups
Early detection and prompt treatment are paramount. Regular follow-ups with an orthopedic specialist, alongside periodic consultations with other healthcare providers, ensure that any signs of non-healing wounds are addressed immediately. For patients at risk, early professional intervention can be the difference between a slow-healing wound and a severe, potentially limb-threatening condition.
Takeaway
The management of diabetic foot wounds, especially those that won’t heal, demands a proactive and multidisciplinary approach. Orthopedic Treatment for Foot Wounds that Won’t Heal in Diabetes is not just about addressing the immediate concern of a wound; it is about safeguarding overall health and mobility. Through specialized interventions like debridement, pressure offloading, and, when necessary, surgical procedures, patients can experience significant improvements and a restoration of quality of life.
Preventing complications begins with daily preventive measures and effective diabetes management. Regular inspections, appropriate footwear, and consistent medical follow-ups ensure that minor issues do not escalate into major health crises.
If you or someone you know is struggling with a diabetic foot wound, consider seeking an expert consultation to explore comprehensive orthopedic treatments that can make a transformative difference. Schedule a consultation with a specialist who understands the intricate challenges of diabetic wounds, and take a vital step towards better foot health and enhanced mobility.