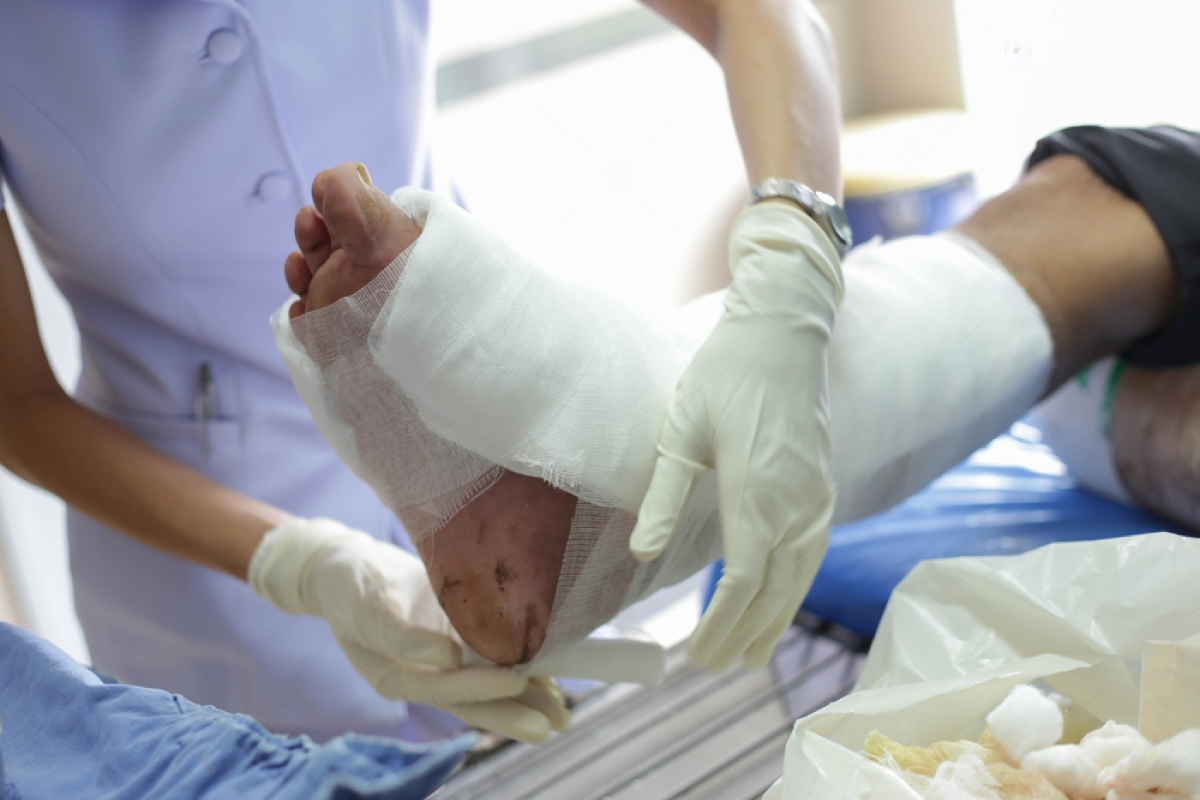
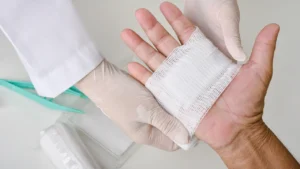
Infected wounds are a serious concern, especially if not treated promptly. Proper orthopedic treatment can significantly enhance the healing process, prevent complications, and restore mobility. In this blog, we’ll explore what infected wounds are, the symptoms to watch for, the role of orthopedic care, and how to prevent infections from occurring in the first place.
What Are Infected Wounds?
Infected wounds are injuries or surgical sites where bacteria, fungi, or other pathogens enter the body, causing infection. This can happen due to an open cut, scrape, surgical incision, or even a pre-existing condition like diabetes that affects wound healing. Common causes of infected wounds include:
- Injury: Trauma leading to cuts or punctures can expose the body to infection.
- Surgery: Post-operative wounds are particularly susceptible to infection if not properly cared for.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Diseases like diabetes or compromised immune systems can increase the likelihood of infection.
Infected wounds can cause pain, swelling, redness, and even systemic symptoms like fever if left untreated. Without proper care, infections can worsen, leading to more severe complications.
Symptoms of Infected Wounds
Recognizing the symptoms of an infected wound is crucial for early treatment. Here are the key signs to look out for:
- Redness and Swelling: These are the body’s natural inflammatory responses to infection.
- Pain: Increased pain around the wound site that doesn’t improve with regular care.
- Discharge or Pus: Yellow, green, or foul-smelling discharge is a strong indication of infection.
- Warmth around the Wound: Infected areas often feel warm to the touch due to inflammation.
- Fever: Systemic signs such as fever may indicate that the infection has spread.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the infection from spreading and causing more severe complications.
How Orthopedic Treatment Helps with Infected Wounds
Orthopedic care plays a key role in the treatment and management of infected wounds, especially when the wound affects the muscles, bones, or joints. Orthopedic specialists are trained to treat wounds that are more complex or involve deeper tissues. Here’s how orthopedic treatment helps:
- Antibiotics: Oral or intravenous antibiotics may be prescribed to fight the infection.
- Wound Debridement: This process involves the removal of dead tissue from the wound to promote healing and reduce the risk of infection.
- Drainage: In some cases, infected wounds may require drainage to remove pus or fluid buildup.
- Surgical Intervention: If the infection is severe or has spread to deeper tissues, surgery may be necessary to remove infected tissue or repair damaged structures.
Orthopedic treatment helps ensure that the infection is controlled and the wound heals properly, minimizing long-term damage and restoring mobility.
Risks of Untreated Infected Wounds
Failing to properly treat an infected wound can lead to serious complications. Here are some of the risks associated with untreated infected wounds:
- Sepsis: A life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s response to infection causes widespread inflammation.
- Tissue Damage: The infection can damage surrounding tissues, muscles, and even bones, leading to permanent impairments.
- Impaired Mobility: Infected wounds, especially those near joints, can limit movement and lead to long-term mobility issues.
- Chronic Infections: Untreated infections may become chronic, requiring more extensive and costly treatments over time.
Orthopedic care is essential to prevent these complications and ensure that infections are managed effectively and promptly.
Steps to Treat Infected Wounds in Orthopedic Care
Treating an infected wound involves several key steps to ensure that the infection is controlled and healing is optimized. Here’s the general process:
- Assessment: The orthopedic specialist evaluates the wound to determine the severity of the infection and whether deeper structures are involved.
- Cleaning: The wound is cleaned thoroughly to remove dirt, bacteria, and debris. This may involve irrigation with saline or antiseptic solutions.
- Debridement: If necessary, dead or infected tissue is removed to prevent further spread of the infection.
- Antibiotic Treatment: Depending on the severity of the infection, oral or IV antibiotics are prescribed to fight the infection.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: The wound is monitored for signs of healing, and follow-up appointments may be scheduled to ensure that the infection does not recur.
By following these steps, orthopedic specialists help reduce the risk of complications and support the healing process.
Preventing Infected Wounds: Best Practices
Prevention is always better than treatment. Here are some tips to reduce the risk of developing infected wounds:
- Proper Wound Care: Always clean and cover wounds properly to prevent contamination.
- Post-Surgery Care: Follow your surgeon’s aftercare instructions to minimize the risk of infection after surgery.
- Good Hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly before touching a wound and use clean materials when dressing it.
- Manage Pre-existing Conditions: If you have conditions like diabetes, make sure they are well-controlled to support proper wound healing.
By following these preventive measures, you can greatly reduce your chances of developing an infected wound.
Takeaway
Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is crucial for promoting healing, preventing complications, and restoring mobility. If you notice signs of infection in a wound, it’s important to seek prompt medical attention to avoid serious health risks. An orthopedic specialist can help you manage your wound effectively and ensure the best possible outcome.