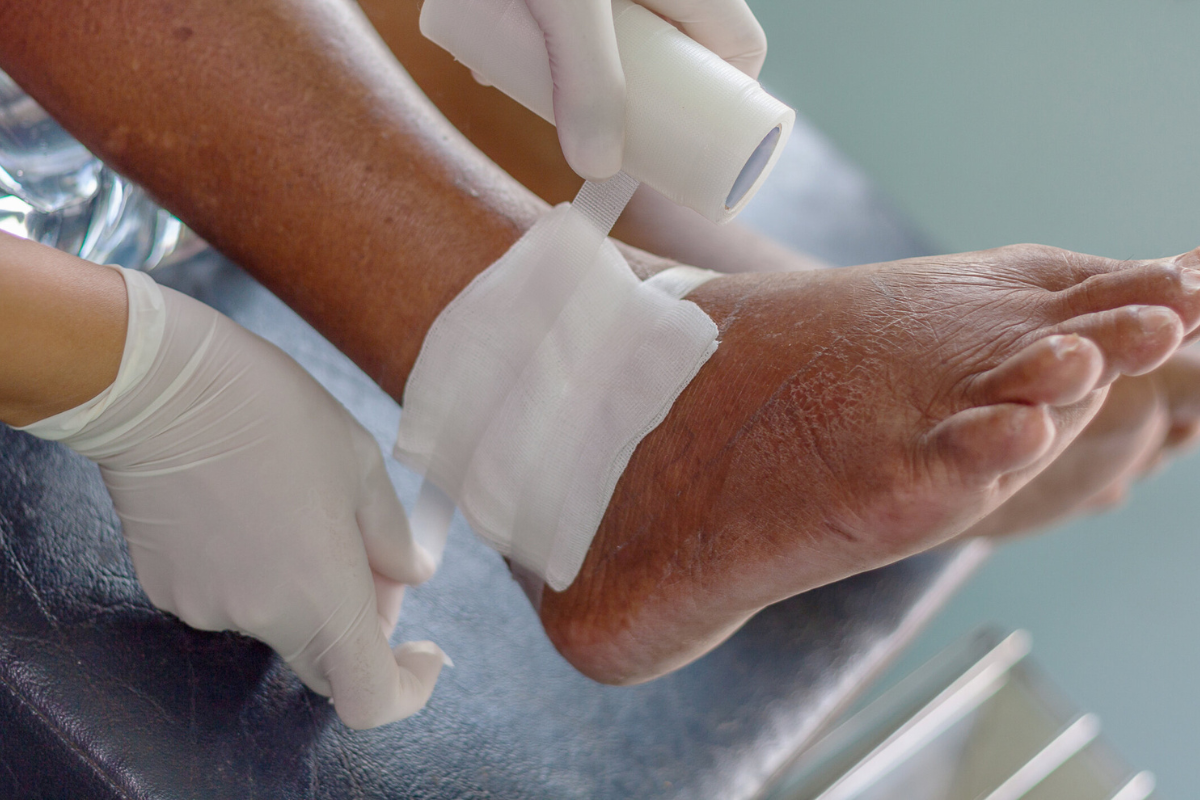
Understanding Non-Healing Wounds
Wounds are expected to follow a natural healing process, but when recovery stalls or the wound does not improve after several weeks, it becomes a non-healing wound. These types of wounds are different from typical cuts, scrapes, or surgical incisions that normally recover within a predictable timeframe. Non-healing wounds often linger due to underlying medical conditions, infection, or reduced blood supply to the affected area. Diabetes, vascular issues, and poor immune responses are among the most common contributors. If untreated, these wounds can lead to severe complications such as chronic pain, loss of function, and even systemic infection. Patients often experience frustration when regular wound care methods fail to deliver results. This is why seeking specialized medical evaluation becomes essential, particularly with an emphasis on Orthopedic Treatment for Non-Healing Wounds.
Why Orthopedic Specialists Address Non-Healing Wounds
Orthopedic care is usually associated with bones, joints, and muscles, but it also plays an essential role in managing complex wounds that do not heal. These specialists look at the wound in relation to structural stability, blood flow, and mobility—factors that are vital for recovery. Orthopedic doctors often work alongside wound care experts, vascular surgeons, and infectious disease specialists to deliver comprehensive care. Their involvement becomes particularly important when wounds are close to joints, bones, or areas under repetitive stress. Preventing complications such as osteomyelitis, which is an infection of the bone, requires orthopedic insight and intervention. By addressing both the musculoskeletal aspects and the wound itself, orthopedists create treatment plans that restore mobility while supporting proper healing. This integrated approach ensures that patients benefit from a more complete level of care, rather than focusing solely on the surface of the wound.
Common Conditions Leading to Non-Healing Wounds
Several medical and physical conditions make certain individuals more prone to developing wounds that resist healing. Diabetes is one of the most significant causes, particularly due to poor circulation and nerve damage in the feet. Peripheral artery disease also plays a large role since restricted blood flow prevents vital nutrients and oxygen from reaching the wound site. Patients with limited mobility, such as those who are bedridden or recovering from surgery, may suffer from pressure ulcers that become non-healing if not managed properly. Post-surgical wounds, especially after orthopedic procedures, can also struggle to recover if there are infections or underlying health issues. Even fractures that are improperly supported may contribute to wound problems. By recognizing these contributing conditions, patients and caregivers can better understand why orthopedic assessment is crucial. An orthopedic perspective ensures that these systemic and structural challenges are identified and addressed early.
Orthopedic Diagnostic Approaches
An orthopedic evaluation of non-healing wounds goes beyond basic inspection. Doctors perform thorough physical examinations to check for underlying musculoskeletal problems that may interfere with healing. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans are used to determine if the wound has affected the surrounding bone or soft tissues. Laboratory testing may also be ordered to identify infections, nutrient deficiencies, or systemic conditions hindering recovery. Orthopedic specialists often use advanced wound assessment tools to measure tissue health, circulation, and pressure points. These diagnostics allow them to detect hidden issues, such as poor alignment or restricted movement, that contribute to delayed healing. The comprehensive evaluation ensures that the chosen treatment strategy is both targeted and effective. Without this level of detailed assessment, treatment may fail to address the real reasons behind the non-healing wound.
Orthopedic Treatment Options for Non-Healing Wounds
Orthopedic Treatment for Non-Healing Wounds encompasses a wide range of specialized methods. Surgical interventions are sometimes necessary, including wound debridement to remove dead tissue or skin grafting to cover large areas that cannot heal naturally. Stabilizing nearby fractures or correcting deformities with orthopedic surgery can also create conditions more favorable for healing. Orthopedic devices such as braces, casts, and offloading boots are often prescribed to reduce pressure on wounds and protect them from further damage. Advanced wound dressings guided by orthopedic care may include moisture-balancing materials, antimicrobial solutions, and biologically active substances that support tissue regeneration. Physical therapy is also incorporated to enhance blood circulation and encourage mobility without worsening the wound. These treatment options are carefully chosen to ensure that the wound heals while preserving musculoskeletal function. Patients benefit from a tailored approach that goes beyond temporary relief and promotes long-term recovery.
Innovative Orthopedic Solutions in Wound Healing
Orthopedic practices continue to adopt new technologies that improve wound healing outcomes. Negative pressure wound therapy is one example, where suction devices are used to remove excess fluids and promote faster tissue repair. Orthopedic specialists also work with bioengineered tissues and regenerative medicine, which provide new layers of protection and encourage natural skin and tissue growth. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, while often coordinated with other specialists, may also be integrated into orthopedic wound management, delivering concentrated oxygen that boosts healing at the cellular level. These innovative approaches have proven effective, particularly for patients who have struggled with chronic wounds for months or years. Orthopedic researchers are constantly exploring new combinations of surgical techniques, biologic materials, and rehabilitation programs. The goal is to make recovery faster, safer, and less prone to recurrence. Patients who once faced limited options now benefit from an expanding range of orthopedic treatments specifically designed for persistent wounds.
Benefits of Orthopedic Treatment for Non-Healing Wounds
Choosing orthopedic care provides patients with a more comprehensive path to healing. Unlike general wound management, orthopedic treatment takes musculoskeletal function into account, ensuring that healing aligns with improved mobility and daily activity. Faster wound recovery is one of the most noticeable benefits, often reducing the need for repeated hospital visits. Infection risks, particularly those that can spread into the bone, are significantly reduced under orthopedic supervision. Patients experience greater independence as wounds heal in ways that support walking, movement, and strength. Another advantage is that orthopedic doctors focus on preventing wound recurrence, ensuring that the structural or pressure-related issues that caused the problem are resolved. The holistic effect of orthopedic care improves both physical well-being and quality of life. For many patients, this means less discomfort, fewer complications, and greater peace of mind.
How to Know When to Seek Orthopedic Help
Recognizing when to see an orthopedic doctor for non-healing wounds can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Any wound that persists beyond six to eight weeks without noticeable improvement should be evaluated. Warning signs include swelling, redness, foul odor, and visible bone or tendon. If a wound becomes increasingly painful or produces discharge, medical intervention is urgently required. Patients who notice that traditional wound care is no longer effective should not delay seeking orthopedic consultation. Those with conditions like diabetes or vascular disease should be especially proactive since their risk of complications is higher. Orthopedic specialists have the expertise to diagnose whether the wound has affected underlying structures such as bone or cartilage. By seeking care early, patients greatly increase the chances of saving both limb and overall health.
Preventive Orthopedic Care for At-Risk Patients
Preventive strategies play a key role in reducing the chances of developing non-healing wounds. Orthopedic doctors often recommend specialized footwear and pressure-relieving devices for diabetic patients to reduce the risk of ulcers. After surgery, consistent monitoring ensures wounds recover without infection or mechanical stress. Orthopedic teams also provide lifestyle recommendations, including proper nutrition, gentle exercise, and techniques to maintain healthy circulation. Regular follow-up appointments allow early detection of potential problems before they escalate. Patients with limited mobility may also benefit from repositioning schedules or support surfaces that protect vulnerable areas. The goal of preventive orthopedic care is not only to heal wounds but also to stop them from returning. By addressing both the immediate wound and the long-term risk factors, orthopedics gives patients stronger tools for ongoing health.
FAQ Section
Q1: How does an orthopedic doctor help with non-healing wounds?
Orthopedic doctors provide specialized care by addressing the musculoskeletal and structural issues that interfere with wound healing. They offer surgical and non-surgical solutions that restore stability, reduce pressure, and promote circulation, leading to improved recovery outcomes.
Q2: What is the difference between seeing a wound care specialist and an orthopedic specialist?
A wound care specialist focuses on direct wound management, while an orthopedic doctor looks at how bones, joints, and movement affect healing. In many cases, both types of specialists work together to provide comprehensive care.
Q3: Can orthopedic treatment prevent amputation in severe wound cases?
Yes, orthopedic treatment often plays a critical role in preventing amputation by stabilizing bones, treating infections, and ensuring wounds heal properly. Early intervention significantly lowers the risk of losing a limb.
Q4: What advanced technologies are used by orthopedics for wound management?
Orthopedic doctors may use negative pressure wound therapy, bioengineered tissues, regenerative medicine, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy to improve outcomes for non-healing wounds.
Q5: When should I consider orthopedic consultation for my chronic wound?
If a wound shows no improvement after six to eight weeks, becomes infected, or exposes deeper tissues such as bone, it is essential to seek orthopedic consultation immediately.